CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture
1、Future和Callable接口
Future接口定义了操作异步任务执行一些方法,如获取异步任务的执行结果、取消任务的执行、判断任务是否被取消、判断任务执行是否完毕等。
Callable接口中定义了需要有返回的任务需要实现的方法。
比如主线程让一个子线程去执行任务,子线程可能比较耗时,启动子线程开始执行任务后,主线程就去做其他事情了,过了一会才去获取子任务的执行结果。
2、FutureTask
本源的Future接口相关架构
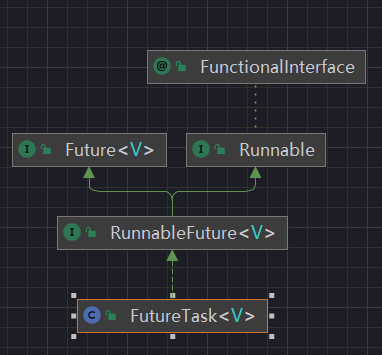
get()阻塞
@Test
public void demo01() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(() -> {
System.out.println("-----come in FutureTask");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100);
});
Thread t1 = new Thread(futureTask, "t1");
t1.start();
//3秒钟后才出来结果,还没有计算你提前来拿(只要一调用get方法,对于结果就是不见不散,会导致阻塞)
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+futureTask.get());
//3秒钟后才出来结果,我只想等待1秒钟,过时不候
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + futureTask.get(1L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + " run... here");
}
打印结果
-----come in FutureTask
java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException
一旦调用get()方法,不管是否计算完成都会导致阻塞,o(╥﹏╥)o
isDone()轮询
- 轮询的方式会耗费无谓的CPU资源,而且也不见得能及时地得到计算结果.
- 如果想要异步获取结果,通常都会以轮询的方式去获取结果尽量不要阻塞
@Test
public void demo02() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(() -> {
System.out.println("-----come in FutureTask");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "" + ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100);
});
new Thread(futureTask, "t1").start();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "线程完成任务");
/**
* 用于阻塞式获取结果,如果想要异步获取结果,通常都会以轮询的方式去获取结果
*/
while (true) {
if (futureTask.isDone()) {
System.out.println(futureTask.get());
break;
}
}
}
打印结果
main 线程完成任务
-----come in FutureTask
73
小总结
- 不见不散,过时不候,轮询
- 想完成一些复杂的任务
- 应对Future的完成时间,完成了可以告诉我,也就是我们的回调通知
- 将两个异步计算合成一个异步计算,这两个异步计算互相独立,同时第二个又依赖第一个的结果。
- 当Future集合中某个任务最快结束时,返回结果。等待Future结合中的所有任务都完成。
3、CompletableFuture
- 阻塞的方式和异步编程的设计理念相违背,而轮询的方式会消耗无畏的CPU资源。因此,JDK8设计出CompletableFuture
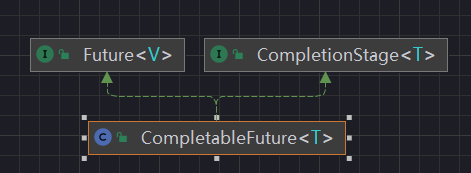
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> {
类架构说明
3.1、CompletionStage接口

代表异步计算过程中的某一个阶段,一个阶段完成以后可能会触发另外一个阶段,有些类似Linux系统的管道分隔符传参数。
一个阶段的计算执行可以是一个Function, Consumer或者Runnable。比如:stage.then Apply(x->square(x) ) .then Accept
(x->System.out.print(x) ) .then Run() ->System.out.print In() )
一个阶段的执行可能是被单个阶段的完成触发,也可能是由多个阶段一起触发。
3.2、CompletableFuture类
在Java 8中, Complet able Future提供了非常强大的Future的扩展功能, 可以帮助我们简化异步编程的复杂性, 并且提供了函数式编程的能 力, 可以通过回调的方式处理计算结果, 也提供了转换和组合Complet able Future的方法。
它可能代表一个明确完成的Future, 也有可能代表一个完成阶段(Completion Stage) , 它支持在计算完成以后触发一些函数或执行某些 动作。
它实现了Future和Completion Stage接口
4、CompletableFuture核心的四个静态方法
利用核心的四个静态方法创建一个异步操作 | 不建议用new
关键就是 |有没有返回值|是否用了线程池|
参数说明:
没有指定Executor的方法,直接使用默认的
ForkJoinPool.commPool()作为它的线程池执行异步代码。如果指定线程池,则使用我们定义的或者特别指定的线程池执行异步代码。
4.1、runAsync 无 返回值
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable) {
return asyncRunStage(asyncPool, runnable);
}
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable,Executor executor) {
return asyncRunStage(screenExecutor(executor), runnable);
}
4.2、supplyAsync 有 返回值
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) {
return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier);
}
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor) {
return asyncSupplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), supplier);
}
4.3、上述Executor executor参数说明
- 没有指定Executor的方法,直接使用默认的ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码。
- 如果指定线程池,则使用我们自定义的或者特别指定的线程池执行异步代码
4.4、Code
runAsync
/**
* runAsync
* 无返回值
*
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Test
public void demo01() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "-----come in");//ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9 -----come in
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("-----task is over");//-----task is over
});
System.out.println(future.get());//null
}
/**
* runAsync 结合线程池
* 无返回值
*
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Test
public void demo02() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "-----come in");//pool-1-thread-1 -----come in
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("-----task is over");//-----task is over
}, executorService);
System.out.println(future.get());//null
executorService.shutdown();
}
supplyAsync
/**
* supplyAsync 有返回值
*
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Test
public void demo03() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "-----come in");//ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9 -----come in
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100);
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());//5
}
/**
* supplyAsync 有返回值
*
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Test
public void demo04() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "-----come in");//pool-1-thread-1 -----come in
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100);
}, executorService);
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());//83
executorService.shutdown();
}
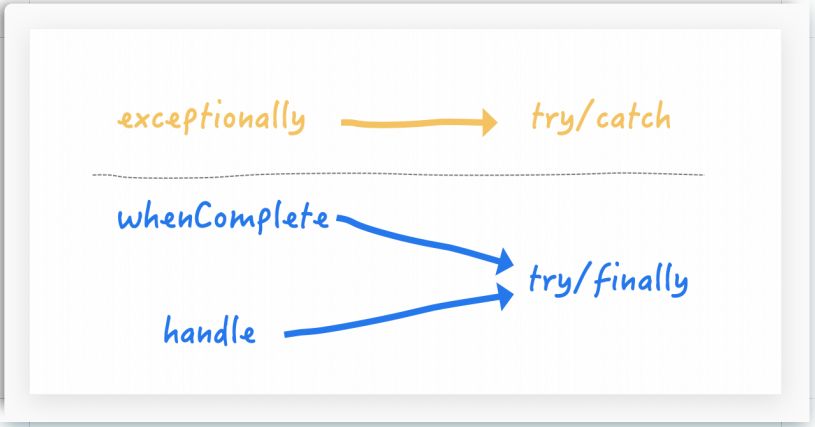
whenComplete和exceptionally
从Java8开始引入了CompletableFuture,它是Future的功能增强版,可以传入回调对象,当异步任务完成或者发生异常时,自动调用回调对象的回调方法
- 使用默认线程池
/**
* whenComplete
* 从Java8开始引入了CompletableFuture,它是Future的功能增强版。
* 可以传入回调对象,当异步任务完成或者发生异常时,自动调用回调对象的回调方法
*/
@Test
public void demo05() {
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "-----come in");//ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9 -----come in
int result = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(10);
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("-----计算结束耗时1秒钟,result: " + result);//-----计算结束耗时1秒钟,result: 7
if (result > 6) {
int age = 10 / 0;
}
return result;
}).whenComplete((v, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("-----result: " + v);
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {
System.out.println("-----exception: " + e.getCause() + "\t" + e.getMessage());//-----exception: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
return -44;
});
//主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:暂停3秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
- 使用自定义线程池
@Test
public void demo06() {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
try {
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "-----come in");//pool-1-thread-1 -----come in
int result = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(10);
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("-----计算结束耗时1秒钟,result: " + result);//-----计算结束耗时1秒钟,result: 1
if (result > 6) {
int age = 10 / 0;
}
return result;
}, executorService).whenComplete((v, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("-----result: " + v);//-----result: 1
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("-----exception: " + e.getCause() + "\t" + e.getMessage());
return -44;
});
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
executorService.shutdown();
}
//主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:暂停3秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
CompletableFuture的优点
- 异步任务结束时,会自动回调某个对象的方法;
- 异步任务出错时,会自动回调某个对象的方法;
- 主线程设置好回调后,不再关心异步任务的执行,异步任务之间可以顺序执行
5、电商比价案例
5.1、函数式编程已经主流
Lambda +Stream+链式调用+Java8函数式编程
- Runnable

image-20220821164331393
- Function

image-20220821164349674
- Consumer

image-20220821164359454
- Supplier
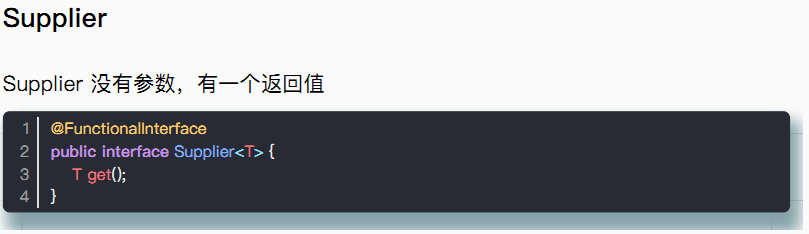
image-20220821164407186
- BiConsumer

image-20220821164416574
- 小总结
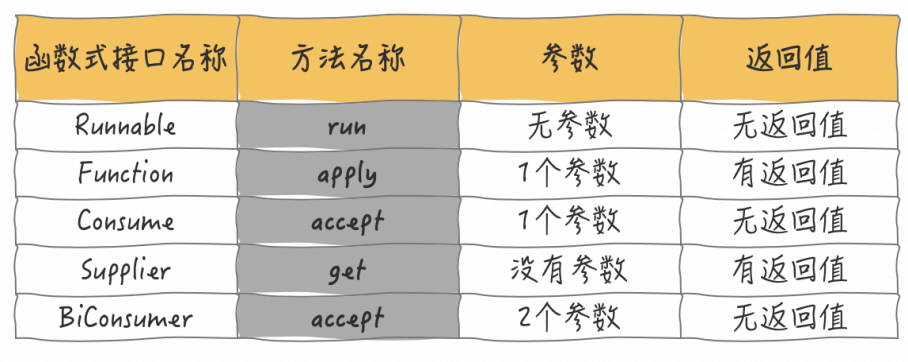
image-20220821164454326
| 函数式接口名称 | 方法名称 | 参数 | 返回值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Runnable | run | 无参数 | 无返回值 |
| Function | apply | 1个参数 | 有返回值 |
| Consume | accept | 1个参数 | 无返回值 |
| Supplier | get | 没有参数 | 有返回值 |
| Biconsumer | accept | 2个参数 | 无返回值 |
5.2、join和get对比
- 功能几乎一样,区别在于编码时是否需要抛出异常
- get()方法需要抛出异常
- join()方法不需要抛出异常
public class Chain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//抛出异常
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return "hello 12345";
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
}
}
public class Chain {
public static void main(String[] args) {//未抛出异常
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return "hello 12345";
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.join());
}
}
5.3、大厂业务需求说明
经常出现在等待某条 SQL 执行完成后,再继续执行下一条 SQL ,而这两条 SQL 本身是并无关系的,可以同时进行执行的。
我们希望能够两条 SQL 同时进行处理,而不是等待其中的某一条 SQL 完成后,再继续下一条。同理, 对于分布式微服务的调用,按照实际业务,如果是无关联step by step的业务,可以尝试是否可以多箭齐发,同时调用。
我们去比同一个商品在各个平台上的价格,要求获得一个清单列表,
- step by step,查完京东查淘宝,查完淘宝查天猫......
- all 一口气同时查询。。。。。
5.4、一波流Java8函数式编程带走
/**
* 案例说明:电商比价需求,模拟如下情况:
* <p>
* 1需求:
* 1.1 同一款产品,同时搜索出同款产品在各大电商平台的售价;
* 1.2 同一款产品,同时搜索出本产品在同一个电商平台下,各个入驻卖家售价是多少
* <p>
* 2输出:出来结果希望是同款产品的在不同地方的价格清单列表,返回一个List<String>
* 《mysql》 in jd price is 88.05
* 《mysql》 in dangdang price is 86.11
* 《mysql》 in taobao price is 90.43
* <p>
* 3 技术要求
* 3.1 函数式编程
* 3.2 链式编程
* 3.3 Stream流式计算
*/
public class CompletableFutureDemo2 {
static List<NetMall> list = Arrays.asList(
new NetMall("jd"),
new NetMall("tmall"),
new NetMall("pdd"),
new NetMall("mi")
);
/**
* step by step 一家家搜查
* List<NetMall> ----->map------> List<String>
*
* @param list
* @param productName
* @return
*/
public static List<String> getPrice(List<NetMall> list, String productName) {
//《mysql》 in taobao price is 90.43
return list.stream().map(netMall ->
String.format(productName + " in %s price is %.2f",
netMall.getNetMallName(),
netMall.calcPrice(productName)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* List<NetMall> ----->List<CompletableFuture<String>>------> List<String>
*
* @param list
* @param productName
* @return
*/
public static List<String> getPriceByCompletableFuture(List<NetMall> list, String productName) {
return list.stream().map(netMall ->
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> String.format(productName + " in %s price is %.2f",
netMall.getNetMallName(),
netMall.calcPrice(productName))))
.collect(Collectors.toList())
.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<String> list1 = getPrice(list, "mysql");
for (String element : list1) {
System.out.println(element);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----costTime: " + (endTime - startTime) + " 毫秒");
System.out.println("--------------------");
long startTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<String> list2 = getPriceByCompletableFuture(list, "mysql");
for (String element : list2) {
System.out.println(element);
}
long endTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----costTime: " + (endTime2 - startTime2) + " 毫秒");
}
}
class NetMall {
@Getter
private String netMallName;
public NetMall(String netMallName) {
this.netMallName = netMallName;
}
public double calcPrice(String productName) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble() * 2 + productName.charAt(0);
}
}
打印结果
mysql in jd price is 109.80
mysql in tmall price is 110.16
mysql in pdd price is 110.99
mysql in mi price is 109.56
----costTime: 4113 毫秒
--------------------
mysql in jd price is 109.78
mysql in tmall price is 110.86
mysql in pdd price is 110.32
mysql in mi price is 109.86
----costTime: 1015 毫秒
6、CompletableFuture常用方法
6.1、获得结果和触发计算
获取结果
public T get() 不见不散,容易阻塞
public T get(long timeout,TimeUnit unit) 过时不候,超过时间会爆异常
public T join() 类似于get(),区别在于是否需要抛出异常
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)
没有计算完成的情况下,给一个替代结果
立即获取结果不阻塞
计算完,返回计算完成后的结果
没算完,返回设定的valueAbsent(直接返回了备胎值xxx)
public T get()
不见不散
public T get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
Object r;
return reportGet((r = result) == null ? waitingGet(true) : r);
}
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
过时不候,超过时间会抛异常【java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException】
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
Object r;
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
return reportGet((r = result) == null ? timedGet(nanos) : r);
}
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)
- 没有计算完成的情况下,给我一个替代结果
- 立即获取结果不阻塞
- 计算完,返回计算完成后的结果
- 没算完,返回设定的valueIfAbsent值
/**
* 获得结果和触发计算
* <p>
* 1.不见不散
* public T get()
* <p>
* 2. 过时不候
* public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
* <p>
* public T join()
* <p>
* 3.没有计算完成的情况下,给我一个替代结果
* // 立即获取结果不阻塞 计算完,返回计算完成后的结果 没算完,返回设定的valueIfAbsent值
* public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)
* <p>
* 4.是否打断get方法立即返回括号值
* public boolean complete(T value)
*
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Test
public void demo01() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 533;
});
//去掉注释上面计算没有完成,返回444
//开启注释上满计算完成,返回计算结果
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());//533
// System.out.println(completableFuture.join());//533
// 没有计算完成的情况下,给我一个替代结果
// 立即获取结果不阻塞 计算完,返回计算完成后的结果 没算完,返回设定的valueIfAbsent值
System.out.println(completableFuture.getNow(444));//533
// join
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Jin").thenApply(r -> r + "666").join());//Jin666
}
主动触发计算
public boolean complete(T value)
是否打断get方法立即返回括号值
@Test
public void demo02() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 533;
});
//注释掉暂停线程,get还没有算完只能返回complete方法设置的444;暂停2秒钟线程,异步线程能够计算完成返回get
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
// TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//当调用CompletableFuture.get()被阻塞的时候,complete方法就是结束阻塞并get()获取设置的complete里面的值.
//执行完成返回false,未执行完成返回true,并返回默认值
//返回false,调用get方法返回533。返回true,调用get方法返回444
boolean complete = completableFuture.complete(444);
System.out.println(complete);
System.out.println(complete + "\t" + completableFuture.get());
}
6.2、对计算结果进行处理
thenApply
计算结果存在依赖关系,这两个线程串行化
由于存在依赖关系(当前步错,不走下一步),当前步骤有异常的话就叫停。
/**
* thenApply:对计算结果进行处理
*/
@Test
public void demo03() {
//当一个线程依赖另一个线程时用 thenApply 方法来把这两个线程串行化,
CompletableFuture<Integer> exceptionally = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("111");
return 1024;
}).thenApply(f -> {
System.out.println("222");
return f + 1;
}).thenApply(f -> {
//int age = 10/0; // 异常情况:那步出错就停在那步。
System.out.println("333");
return f + 1;
}).whenCompleteAsync((v, e) -> {
System.out.println("*****v: " + v);
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
});
System.out.println("-----主线程结束,END");
// 主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("结果值为:" + exceptionally.join());
}
打印结果
-----主线程结束,END
111
222
333
*****v: 1026
结果值为:1026
handle
有异常也可以往下一步走,根据带的异常参数可以进一步处理
/**
* handle 有异常也可以往下一步走,根据带的异常参数可以进一步处理
*/
@Test
public void demo04() {
//当一个线程依赖另一个线程时用 thenApply 方法来把这两个线程串行化,
//当一个线程依赖另一个线程时用 handle 方法来把这两个线程串行化,
// 异常情况:有异常也可以往下一步走,根据带的异常参数可以进一步处理
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("111");
return 1024;
}).handle((f, e) -> {
System.out.println("222");
int age = 10 / 0;
System.out.println("2222");
return f + 1;
}).handle((f, e) -> {
System.out.println("333");
return f + 1;
}).handle((f, e) -> {
System.out.println("444");
return f + 1;
}).whenCompleteAsync((v, e) -> {
System.out.println("*****v: " + v);
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
});
System.out.println("-----主线程结束,END");
// 主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
打印结果
-----主线程结束,END
111
222
333
444
*****v: null
java.util.concurrent.CompletionException

6.3、对计算结果进行消费
接收任务的处理结果,并消费处理,无返回结果
| 方法名 | 方法 | 释义 |
|---|---|---|
| thenRun | thenRun(Runnable runnable) | 任务 A 执行完执行 B,并且 B 不需要 A 的结果 |
| thenAccept | thenAccept(Consumer action) | 任务 A 执行完执行 B,B 需要 A 的结果,但是任务 B 无返回值 |
| thenApply(Function fn) | thenApply(Function fn) | 任务 A 执行完执行 B,B 需要 A 的结果,同时任务 B 有返回值 |
/**
* thenRun,thenAccept 对计算结果进行消费不返回
*/
@Test
public void demo05() {
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "resultA").thenRun(() -> {
}).join());//null
System.out.println("------------------------------");
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "resultA").thenAccept(resultA -> {
}).join());//null
System.out.println("------------------------------");
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "resultA").thenApply(resultA -> resultA + " resultB").join());//resultA resultB
}
6.4、对计算速度进行选用
谁快用谁:applyToEither
/**
* applyToEither:对计算速度进行选用
*/
@Test
public void demo07() {
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "completableFuture1---come in ");//ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9 completableFuture1---come in
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 10;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "completableFuture2---come in ");//ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-2 completableFuture2---come in
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 20;
});
// 比较 哪个现场快,返回哪个线程
CompletableFuture<Integer> thenCombineResult = completableFuture1.applyToEither(completableFuture2, f -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in ");//ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-2 ---come in
System.out.println("执行速度快的线程返回值:" + f);//执行速度快的线程返回值:20
return f + 1;
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + thenCombineResult.join());//main 21
}
6.5、对计算结果进行合并
两个CompletionStage任务都完成后,最终能把两个任务的结果一起交给thenCombine 来处理
先完成的先等着,等待其它分支任务
thenCombine
code标准版,好理解先拆分
/** * thenCombine: 对计算结果进行合并 */ @Test public void demo09() { CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in ");//ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9 ---come in return 10; }); CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in ");//ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9 ---come in return 20; }); CompletableFuture<Integer> thenCombineResult = completableFuture1.thenCombine(completableFuture2, (x, y) -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in ");//main ---come in return x + y; }); System.out.println(thenCombineResult.join());//30 }
code表达式
/** * thenCombine: 对计算结果进行合并 */ @Test public void demo10() { CompletableFuture<Integer> thenCombineResult = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in 1");//ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9 ---come in 1 return 10; }).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in 2");//ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9 ---come in 2 return 20; }), (x, y) -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in 3");//main ---come in 3 return x + y; }).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in 4");//ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9 ---come in 4 return 30; }), (a, b) -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in 5");//main ---come in 5 return a + b; }); System.out.println("-----主线程结束,END");//-----主线程结束,END System.out.println(thenCombineResult.join());//60 // 主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭: try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
7.CompleteFuture和线程池说明(非常重要)
上面的几个方法都有普通版本和后面加Async的版本
以thenRun和thenRunAsync为例,有什么区别?
先看结论
没有传入自定义线程池,都用默认线程池ForkJoinPool
传入了一个自定义线程池如果你执行第一个任务的时候,传入了一个自定义线程池
调用thenRun方法执行第二个任务的时候,则第二个任务和第一个任务是用同一个线程池
调用thenRunAsync执行第二个任务的时候,则第一个任务使用的是你自己传入的线程池,第二个任务使用的是ForkJoin线程池
也有可能处理太快,系统优化切换原则,直接使用main线程处理(把sleep去掉)
案例一:自定义线程池+thenRun
//2-1
public class CompletableFutureAPIDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
System.out.println("1号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "abcd";
},threadPool).thenRun(()->{
try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
System.out.println("2号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(()->{
try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
System.out.println("3号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(()->{
try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
System.out.println("4号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
}
}
//1号任务 pool-1-thread-1
//2号任务 pool-1-thread-1
//3号任务 pool-1-thread-1
//4号任务 pool-1-thread-1
案例二:自定义线程池+thenRunAsync
//2-2
public class CompletableFutureAPIDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
System.out.println("1号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "abcd";
},threadPool).thenRunAsync(()->{
try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
System.out.println("2号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(()->{
try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
System.out.println("3号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(()->{
try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
System.out.println("4号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
}
}
//1号任务 pool-1-thread-1
//2号任务 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9---这里另起炉灶重新调用了默认的ForkJoinPool
//3号任务 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
//4号任务 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9
案例三:自定义线程池+thenRunAsync
public class CompletableFutureAPIDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
// try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
System.out.println("1号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "abcd";
},threadPool).thenRun(()->{
// try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
System.out.println("2号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(()->{
// try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
System.out.println("3号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(()->{
//try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
System.out.println("4号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
}
}
//1号任务 1号任务 pool-1-thread-1
//2号任务 main
//3号任务 main
//4号任务 main
源码
//CompletableFuture.java 2009行
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action) {//传入值是一样的
return uniRunStage(null, action);
}
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(asyncPool, action);//但是这里有个异步的线程池asyncPool
}
//进入asyncPool
private static final boolean useCommonPool =
(ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism() > 1);//一般大于1都是成立的
/**
* Default executor -- ForkJoinPool.commonPool() unless it cannot
* support parallelism.
*/
private static final Executor asyncPool = useCommonPool ?
ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor();//所以这里会调用forkJoin线程池
